LLRL: Location-guided Lesions Representation Learning via Image Generate for Assessing Plant Leaf Diseases Severity. Accurate assessment of plant leaf disease severity is crucial for implementing precision pesticide application, which in turn significantly enhances crop yields. Previous methods primarily rely on global perceptual learning, often leading to the misidentification of non-lesion regions as lesions within complex backgrounds, thereby compromising model accuracy. To address the challenge of background interference, we propose a novel location-guided lesion representation learning method (LLRL) based on image generation to assess the severity of plant leaf diseases. Our approach comprises three key networks: the image generation network (IG-Net), the location-guided lesion representation learning network (LGR-Net), and the hierarchical lesion fusion assessment network (HLFA-Net). IG-Net is designed to construct paired images necessary for LGR-Net by utilizing a diffusion model to generate diseased leaves from healthy ones. First, the LGR-Net facilitates the network's focus on the lesion area by contrasting paired images: healthy and diseased leaves, obtaining a pre-trained dual-branch feature encoder (DBF-Enc) that incorporates lesion-specific prior knowledge, providing focused visual features for HLFA-Net. Second, the HLFA-Net, which shares and freezes the DBF-Enc, further fuses and optimizes the features extracted by DBF-Enc, culminating in a precise classification of disease severity. In addition, we construct an image dataset containing three plant leaf diseases from apple, potato, and tomato plants, with a total of 12,098 photos, to evaluate our approach. Finally, experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing classification models, with at least an improvement of 1% in accuracy for severity assessment, underscoring the efficacy of the LLRL method in accurately identifying the severity of plant leaf diseases.
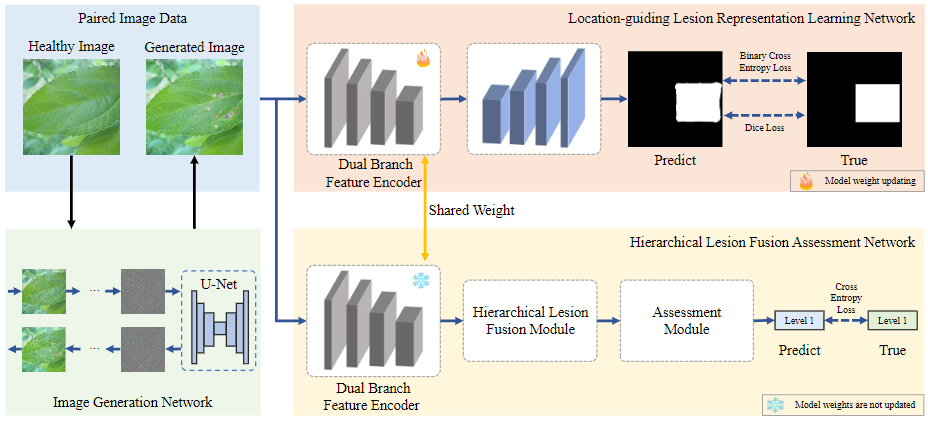
Figure 1: Framework of our approach. The approach consists of an image generation network (IG-Net), location-guided lesion representation learning network (LGR-Net), and hierarchical lesion fusion evaluation network (HLFA-Net).
IG-Net: Image Generation Network. The diffusion model, widely adopted in artificial intelligence applications, has shown impressive results, prompting us to implement it as the Image Generation Network (IG-Net) to create plant healthy-diseased image pairs.
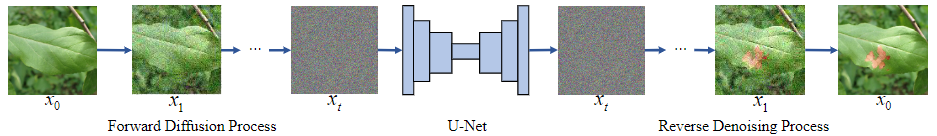
Figure 2: Framework of the Image Generation Network (IG-Net). The diffusion model generates images to create healthy-diseased image pairs.
LGR-Net: Location-guided Lesion Representation Learning Network. We propose the Location-guided Lesion Representation Learning Network (LGR-Net), an Encoder-Decoder-based model with a dual-branch feature encoder (DBF-Enc) and a differential localization decoder (DL-Dec), which enhances the model’s ability to concentrate on disease regions.
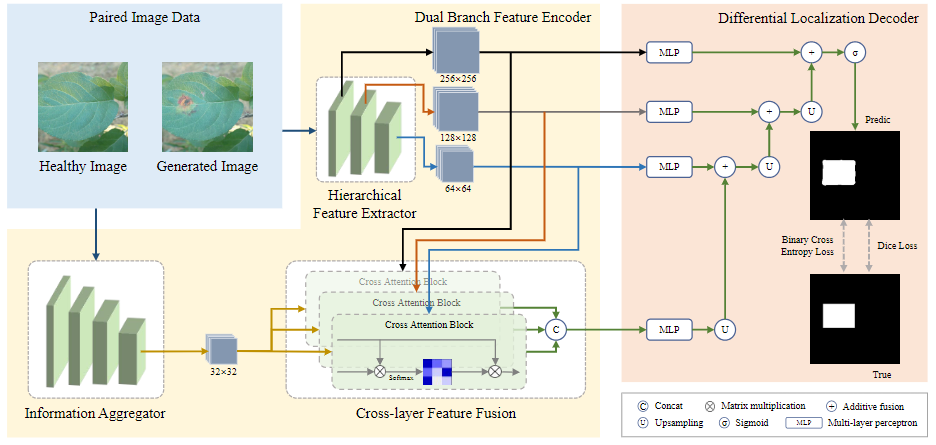
Figure 3: Framework of the Location-guided Lesion Representation Learning Network (LGR-Net). The network consists of a dual-branch feature encoder (DBF-Enc) for feature extraction and a differential localization decoder (DL-Dec) for decoding the region of lesions.
HLFA-Net: Hierarchical Lesions Fusion Assessment Network. We propose the Hierarchical Lesion Fusion Assessment Network (HLFA-Net), which integrates a pre-trained DBF-Enc, a hierarchical lesion fusion module (HLFM), and an assessment module.
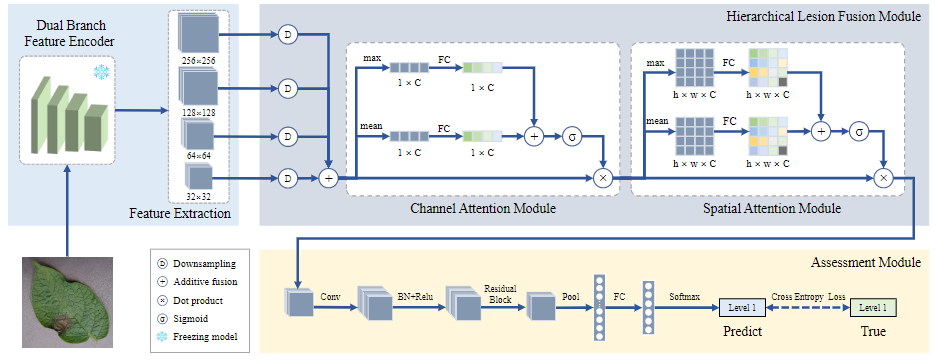
Figure 4: Framework of Hierarchical Lesion Fusion Assessment Network (HLFA-Net). The pre-trained DBF-Enc is used to extract multi-level features focused on lesions, the hierarchical lesions fusion module (HLFM) is used to fuse multi-level features and optimize them using cascade attention mechanisms, and the assessment module is responsible for evaluating the final results.
